Trigger Finger: Key Symptoms And Treatments
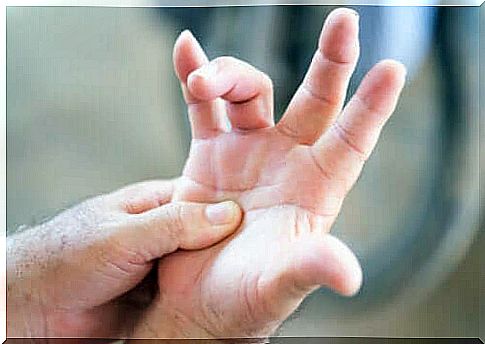
Trigger finger is a condition that limits finger movement and may prevent the finger from flexing. In fact, it tends to get stuck, and to stretch or flex it, you have to snap it, like a spring when it’s tensioned and released.
This anomaly is caused by a problem in the long tendons, also called the flexors . These slide through a kind of tunnel that surrounds them, called the tendon sheath . When this sheath becomes irritated and inflamed, the tunnel narrows and makes movement difficult.
In more severe cases, the trigger finger is stuck in the flexed position and cannot move. This condition is also known as stenosing tenosynovitis and is more common in women and people with diabetes.
Trigger Finger Symptoms
Trigger finger can occur on any finger, including the thumb. It is common to have more than one finger affected, including both hands. The condition is progressive and usually starts with persistent pain at the base of the finger.
The initial symptoms of trigger finger are as follows:
- A lump appears around the base of the finger, towards the palm of the hand.
- The muscle at the base of the finger becomes soft and sensitive to touch.
- There is a stiff feeling in the finger, especially in the early morning hours.
- When you make a move, you hear a click.
As the trigger finger moves forward, it gets stuck in the flexed position and suddenly straightens. In later stages, it locks up and cannot be stretched again.
Diagnosis
The basis for trigger finger diagnosis is the physical examination performed by the physician. Making a movement in the affected area produces a snap, and this is considered a characteristic of the anomaly.
The physical examination is completed by asking the patient to open and close the hand. The palm and base of the fingers will also be checked, inquiring about signs of pain and signs of blockage. After that, the diagnosis can be confirmed.
Trigger Finger Treatments
Trigger finger treatment depends on the state it is in and the time elapsed between the onset of the disease and the medical appointment. Generally speaking, there are three ways to approach it: medication, therapy, and surgery.
Medication
Medications are used to relieve pain and reduce inflammation. This makes moving easier. In general, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs such as ibuprofen, naproxen and the like are prescribed . This measure works to improve symptoms, but it does not solve the problem.
physical therapy
Trigger finger can also be treated with physical therapy measures, such as the following:
- Rest: Activities that involve picking up, holding or using vibrating machines should be avoided for four to six weeks. If you cannot rest, wear a padded glove.
- Splinting: Allows finger to remain extended. It should only be used at night, usually for a month and a half.
- Light Exercises: Some hand stretching exercises may be indicated to improve range of motion.
- Heat and cold: Alternating cold and heat helps reduce inflammation and pain.
- Warm Water Immersion: Dipping your hand in warm water several times a day helps to relax the tendons and relieves symptoms.
Trigger finger surgeries
When medications and physiotherapy don’t work, surgery should be performed. Sometimes, the following procedures are proposed before surgery:
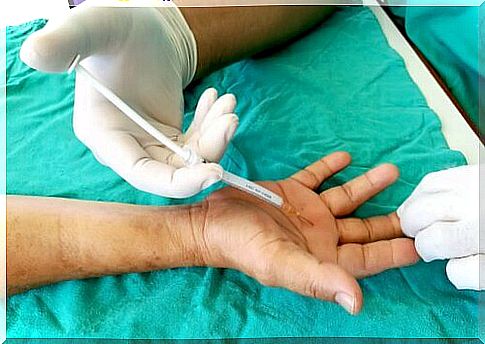
- Steroid Injection : This is applied to the tendon sheath and helps to reduce inflammation. It can be effective for a year or more, but sometimes it is necessary to apply it in more than one session.
- Percutaneous release : consists of inserting a thick needle into the inflamed tendon, after administering anesthesia, and with it undoing the compression that blocks the tendon.
If these procedures do not work, surgical intervention is chosen. This surgery is outpatient and consists of an incision in the compressed area to cut the tendon sheath. The biggest risk is infection or ineffectiveness of the operation.

Risk factors for trigger finger
There are some people who tend to develop trigger finger more easily. Known risk factors are as follows:
- Age: people over 40 and under 60 years old.
- Diseases: being diabetic, suffering from hypothyroidism, suffering from rheumatoid arthritis or having tuberculosis.
- Have had surgery for carpal tunnel syndrome.
- Repetitive activities: carrying out jobs that require repetitive footprints.
A condition with multiple treatments
Trigger finger is a condition that can significantly alter quality of life. The most advisable in these cases is to adapt to the new conditions, avoiding certain movements. If this is impossible in your case, you should consider using effective protections.
None of the available treatments are fully effective. However, a high percentage of patients improve after corticosteroid injections, and there are also successful resolutions with surgery. So the prospects are good.









