Fast Sequence Induction
Rapid sequence induction is orotracheal intubation and is generally used in urgent cases. However, to be effective it is necessary to follow a series of steps in a certain order. If these steps are skipped, they can be life-threatening.
According to a study, “for the physician specializing in emergency medicine, managing the airway in emergency rooms and emergency services is a fundamental part of their basic skills”.
Therefore, it is essential that physicians know how to carry out Rapid Sequence Induction to reduce the risk of pulmonary aspiration that some patients may have.
When is rapid sequence induction performed?
Fast sequence induction is used when a patient arrives at the hospital with an imminent risk of ventilatory failure. A very quick and urgent assessment and the rush to carry out this procedure will prevent it from being carried out with due precision.
The consequences of this can range from hypoxemia to causing damage to the airway when introducing the tracheal tube. Therefore, as urgent as the case requires, it is necessary to remain calm and precisely follow the steps of the procedure.
Although in some cases it is not very clear when tracheal intubation should be performed, which allows rapid sequence induction, if it is suspected that the patient will not be able to keep the airway open, then the procedure should be performed.
However, it is possible to take into account the following symptoms that can clearly indicate the need for rapid sequence induction:
- Suffocating bruise on the neck.
- Thoracic trauma with hypotension.
- Extensive burns.
- Airway obstruction.
- Cardiac arrest.
On top of this, intubation and immediate sedation will also be necessary if the patient is agitated because he is not able to breathe normally. Rapid sequence induction should be practiced as soon as possible.
correct way to proceed
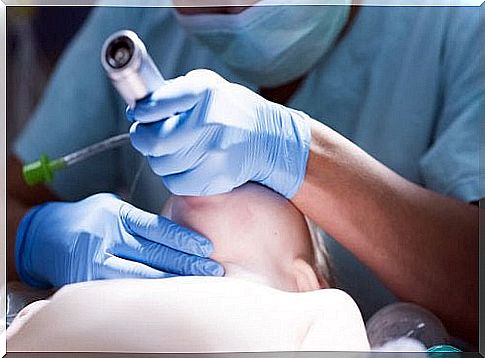
To perform a successful intubation it is necessary to follow a series of steps that will be performed quickly and accurately. In this way, it will be possible to avoid some of the consequences mentioned above.
Actions prior to intubation
- Elevate the patient’s head by placing a pillow underneath.
- Raise the jaw by pressing it up and forward.
- Remove any foreign bodies from the oropharyngeal cavity.
- Aspirate all secretions (blood, vomit).
Fast sequence induction maneuvers
- Hold the laryngoscope with one hand and introduce it through the corner of the mouth, pulling the tongue away and guiding the laryngoscope forward and upward.
- Locate the tip of this instrument on the epiglottis.
- To reduce the risk of bronchoaspiration or regurgitation, another practitioner should perform the Sellick maneuver . This should be done for as long as the intubation lasts.
- In the event that the glottis or vocal chords cannot be visualized, another person must perform the BURP maneuver to expose them. This will allow you to introduce the laryngoscope properly and prevent airway damage.
- When the tube is correctly inserted, the laryngoscope is removed without moving the tube. This will then be fixed and connected to the oxygen source.
Although we have recommended the Sellick and BURP maneuvers, these should never be performed in the event that the patient suffers some trauma or has a foreign body in the trachea. This is very important to take into account.
Fast-frequency induction drugs
It is generally not necessary to use any drug when induction is performed at a rapid rate. However, there are cases in which, without the supply of these drugs, it would be impossible to intubate the patient.
When the patient is restless, it is necessary to administer a sedative medication. In other cases, when you suffer from very intense pain, in addition to the sedative, you have to apply an analgesic.
On rare occasions, emergency physicians should also administer a muscle relaxant. This is essential when the trachea is very tense, making it difficult for the tube to pass.
As we have seen, induction is a procedure that all professionals who are in the medical emergency service must know how to perform correctly in order to avoid possible damage to the airways.