Botulinum Toxin, A Lethal Poison
The botulinum toxin is an exotoxin produced by an anaerobic bacterium called Clostridium botulinum. Exotoxins are molecules secreted extracellularly by some microorganisms capable of causing great damage to the host.
There are different ways to classify these molecules. For example, depending on the tissue they affect, distinguishing between neurotoxins, cardiotoxins, neutrotoxins, among others.
As a general rule, exotoxins are recognized as antigens by the host’s immune system; however, many toxins (as in the case of some pathogenic clostridia) are fatal to the individual before the immune response develops.
The danger of botulinum toxin
It is the most lethal poison existing, surpassing even some artificial compounds developed by the human being. The toxicity of this molecule is 600 million times greater than that of cyanide. A single gram of botulinum toxin would be enough to end the lives of a million guinea pigs.
Such is the magnitude of its toxicity that it has been declared a weapon of mass destruction and prohibited by the Geneva Conventions and the Chemical Weapons Convention, an international arms control treaty signed by most states in the world (192 out of 195 states), with the exception of North Korea, Egypt and South Sudan.
There are seven types of serologically different strains of C. botulinum that produce different types of botulinum: A, B, C, D, E, F and G, with strains C and D being the only ones that produce more than one type of toxin. The most pathogenic toxins are A, B and E.
Only the strains that produce these exotoxins will be able to trigger botulism in humans (occasionally F as well), a very unusual foodborne disease, which is triggered by eating foods intoxicated with these substances.
It is characterized by the progressive loss of muscle function due to botulinum’s neurotoxic effect, which can be fatal if it affects the muscles that mediate respiratory function.
Until relatively recently, mortality from this disease was very high, however, after the discovery of the antidote, it was possible to reduce fatalities by 20%.
Botulinum Action Mechanism
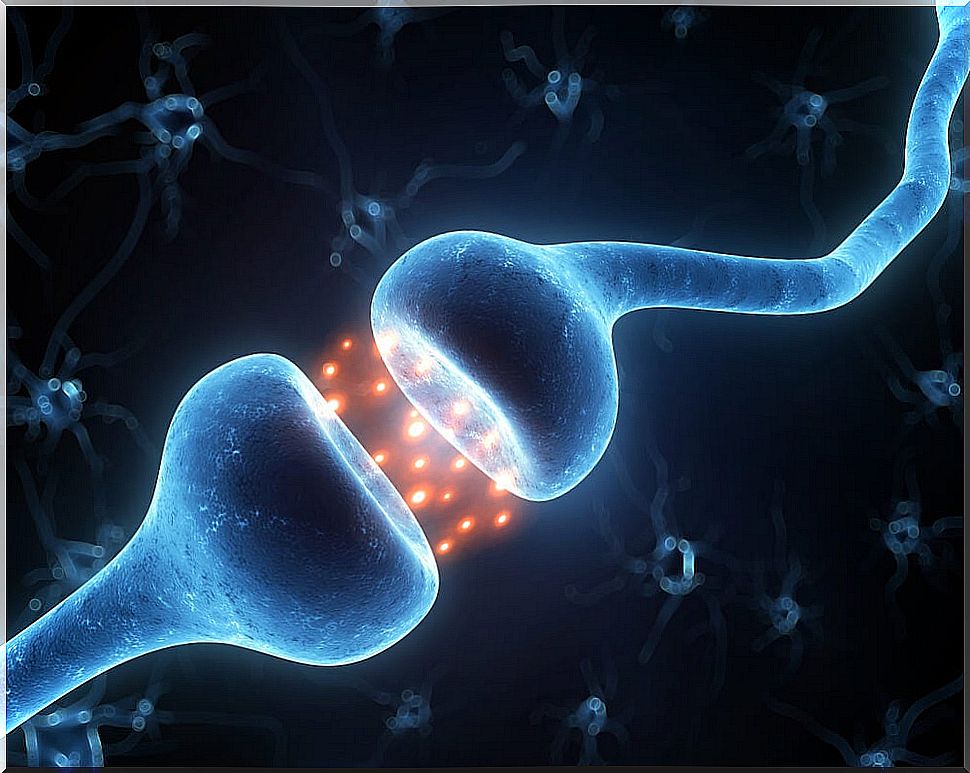
Botulinum has a neurotoxic effect; that is, it attacks the nervous system of the affected individual. To get into context, it will be necessary to remember how a neuronic works and how the transmission of a nevus impulse occurs.
Neurons have two functions: the propagation of the action potential, which is what is known as a nerve impulse, and its transmission to other neurons or to effector cells.
The propagation of the action potential along the neuronal axon is an electrical phenomenon. On the other hand, the transmission of the nerve impulse from one neuron to another or to an effector cell depends on the release of specific neurotransmitters that interact with also specific receptors.
Certain drugs can modify the amount of neurotransmitter released in nerve impulse transmission, something that also happens when you are in love. This is the case with botulinum toxin.
The effector neurons, that is, those in charge of transmitting the nerve impulse to the muscles, are the main target of this toxicant.
Botulinum exerts its action on cholinergic nerve endings, preventing the release of acetylcholine, the main neurotransmitter that mediates muscle contraction. In this way, the affected muscles are completely useless.
Importance of botulinum toxin for medicine
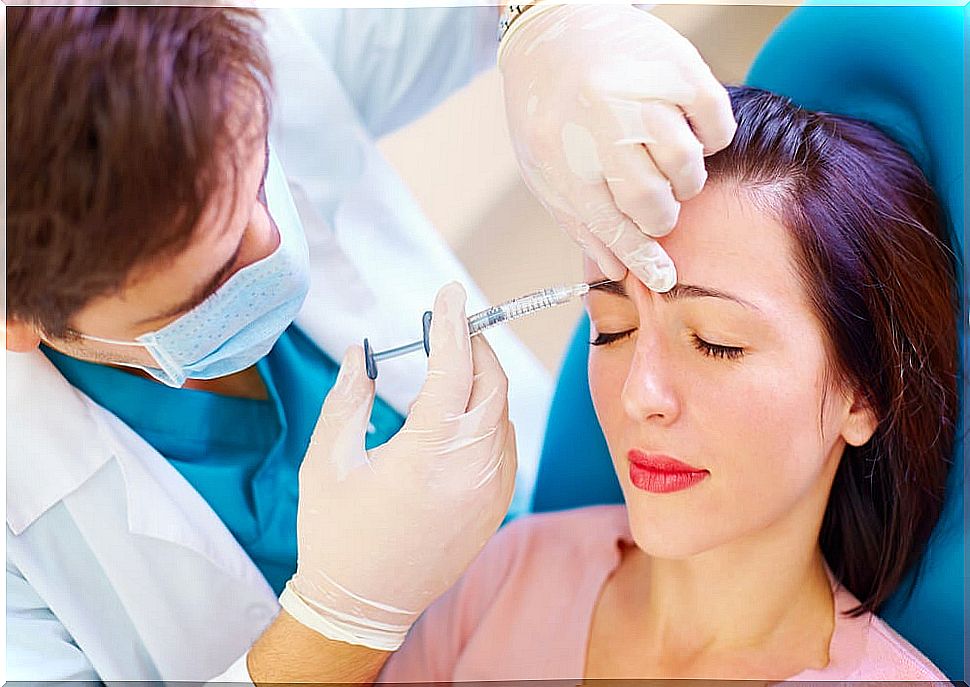
Despite the danger that this toxic poses to humans, two decades ago researchers discovered that using infinitesimal fractions the botulinum toxin had a potent therapeutic power.
Discovering its usefulness in the treatment of spasticity, a disease characterized by chronic involuntary muscle contractions.
If the affected muscle is located and a small amount of botulinum toxin is applied, it is possible to almost completely mitigate muscle spasticity.
However, this is not the only disease for which the toxin is used. The most avant-garde physicians found use in botulinum toxin for the treatment of strabismus, overactive bladder and even migraine.
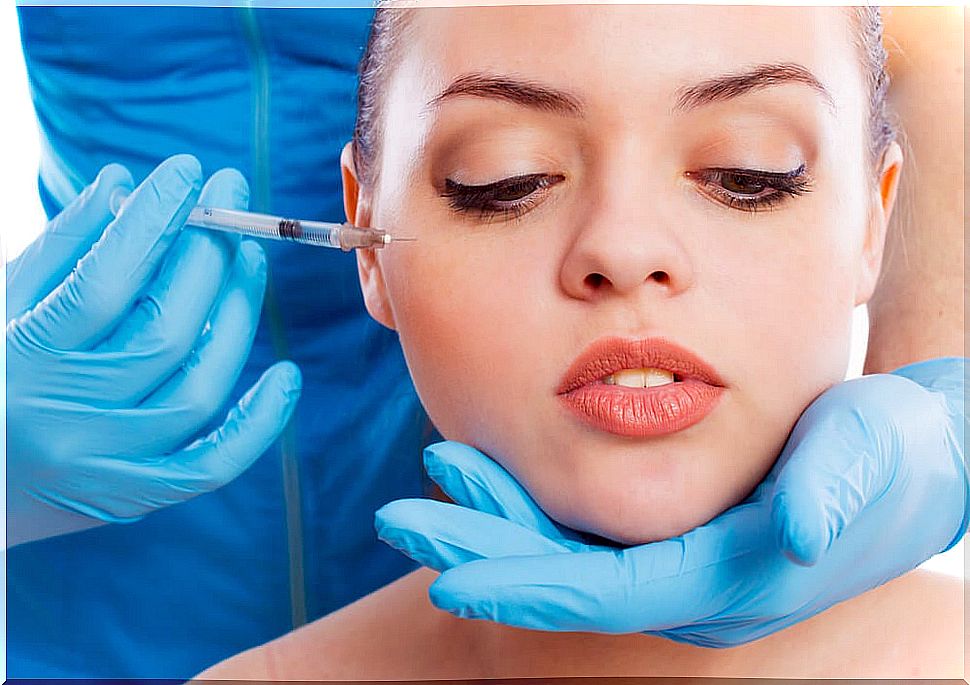
In fact, this substance has become widely popular in the field of aesthetics. The well-known botox is nothing more than the trade name for botulinum toxin type A.
This popularity is due to its power to reduce wrinkles and expression lines for months, applying a minimal amount of botulinum on the muscle responsible for the wrinkles.