Arterial Trunk: Know All About This Disease.
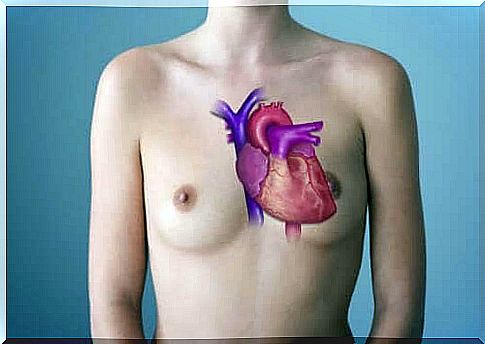
The trunk arteriosus or truncus arteriosus is a congenital malformation in which a single artery arises from the heart and does not have well-formed ventricles and atria.
It is a relatively rare cardiac anomaly, with an incidence of 0.21-0.34% of patients born with a congenital cardiac anomaly and accounting for approximately 2-3% of patients registered in a pediatric cardiac surgery unit.
Causes of the arterial trunk
In a normal heart, blood follows this cycle: body – heart – lung – heart – body. When a person has an arterial trunk, the blood that leaves the heart does not follow this normal cycle.
In these cases, the heart does not have 4 properly separated compartments, but only has one cavity. In this way, there are no atria or ventricles that separate blood according to its origin and destination. There is only one common artery and there is no specific route for blood rich in carbon dioxide or one with oxygenated blood.
The arterial trunk appears during fetal growth, when the baby’s heart is developing. Therefore, this condition is present at the time of birth, that is, we are talking about a congenital problem.
Currently, in most cases, it is not known what triggers this heart problem. However, several factors that can increase the risk of trunk arteriosus are known, including:
- A family history of congenital heart problems.
- Children with chromosomal problems, velocardiofacial syndrome, or DiGeorge syndrome may be at increased risk of developing truncus arteriosus .
- Pregnant women who take certain medications during pregnancy that can harm the fetus.
- Women who contract viral illnesses such as rubella may be more likely to give birth to a baby with an arterial trunk.
What are the symptoms?
Each patient may have different symptoms. However, there are several common symptoms that babies affected by this disease can share. These most common signs are:
- Cyanosis: the skin takes on a bluish purple tone.
- Fatigue.
- Sweat.
- Cold skin.
- Breathing fast and difficult.
- Accelerated heart rate.
- Respiratory congestion.
- Lack of appetite.
All of these symptoms can be common to other medical conditions or other heart problems. Therefore, it is very important to consult the doctor if your child has one of those mentioned in the list.
How can this be diagnosed?
Doctors are often able to diagnose this anomaly before the baby is born. For this they use a fetal echocardiogram. This technique uses sound waves to create an image of the heart in motion.
Thanks to this, you can see what the heart looks like and examine how it works when they are still in the uterus. With the information obtained, doctors plan how to treat the baby immediately after birth.
On the other hand, there is also the pulse oximetry test. It is a simple test that measures the amount of oxygen present in the bloodstream. It might give you the first clue that there’s a heart problem.
Arterial trunk treatment
As a given, studies of the natural history of the arterial trunk suggest a 50% mortality during the first month of life. Thus, survival for the first year of life is 10-25%.
In addition, the vast majority of patients who survive one year of life suffer from severe, often irreversible , pulmonary vascular disease.
As for the treatment, babies need to undergo cardiac surgery in order to avoid possible complications. This operation is usually performed in the first month of life.
During the operation, the aorta and pulmonary arteries are separated, creating a path for blood to travel from the right ventricle to the lungs. The interventricular communication and any other cardiac anomalies detected will be corrected at the same time.